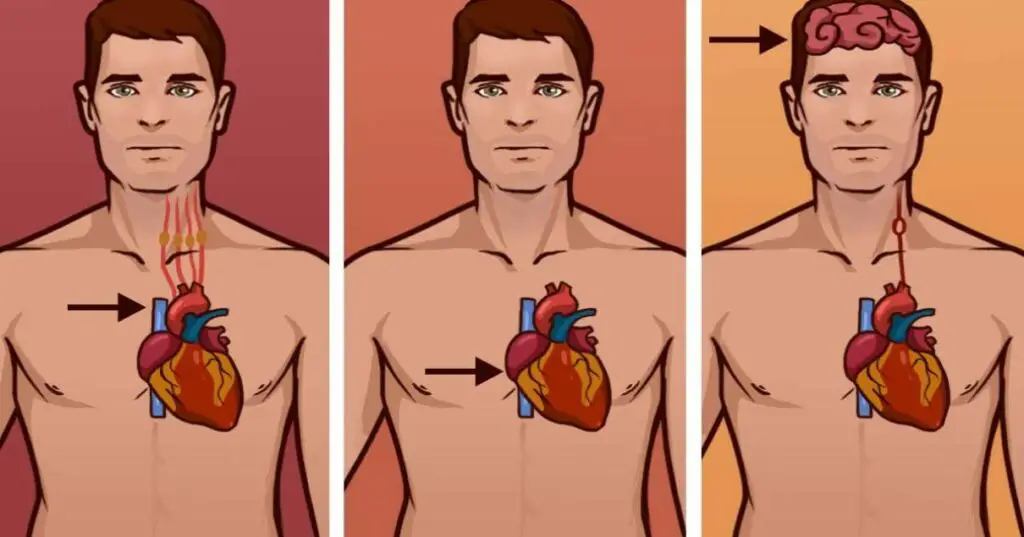
There are several vital distinctions between a heart attack, cardiac arrest, and a stroke that may help to save a life. They all can be life-threatening medical emergencies, but they are not all the same.
In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at each of these conditions and we’ll discuss how to spot the warning signs so that you can get the proper treatment if you or someone you know experiences one.
One of the most essential things to remember is that a blockage in blood flow causes both heart attack and stroke. While the blood is unable to reach the heart in the case of a heart attack, it is prevented from reaching the brain during a stroke. A blood clot generally is the cause of a heart attack, whereas a stroke is usually the result of an obstruction or burst blood vessel – according to Inova Heart and Vascular Institute.
Cardiac Arrest
Although a heart attack can produce cardiac arrest, cardiac arrest is not the same as a heart attack. Cardiac arrest is a devastating and potentially fatal condition affecting more than 350,000 people each year in the United States alone.
The term is used to describe an event in which the heart suddenly stops beating and no blood can reach the brain or other vital organs. This causes the patient to lose consciousness and without immediate treatment, death can occur in as little as a few minutes.
Luckily, there are several effective treatments for cardiac arrest, including CPR (The American Heart Association recommends performing Hands-Only CPR in a way of “Stayin’ Alive” rhythm), electric shocks, as well as using an automated external defibrillator (AED).
However, calling 9-1-1 is of paramount importance. With quick action and proper treatment, those suffering from cardiac arrest can recover fully and go on to live healthy lives. So if you ever encounter this condition firsthand REMEMBER that every second counts!
Heart Attack
It’s well known that chest pain is a symptom of a heart attack. What may not be as well known, however, are the other symptoms that can accompany a heart attack. These can include a tight ache, pressure, or squeezing sensation in the chest, as well as discomfort in the chest, shoulders, arm, and back.
Along with aching in the stomach, shortness of breath, tiredness, tension, lightheadedness, and sweating are all additional indicators of a heart attack. Women are more likely to experience symptoms other than chest pain, such as nausea, vomiting, and pain in the neck or jaw.
Call emergency immediately if you or someone you’re with experiences any of the following symptoms for more than 5 minutes.
Stroke
The three most common stroke symptoms are severe arm or leg weakness, sudden numbness or tingling in the face, and trouble speaking. These three are also known by the acronym “FAST” for Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulty, and Time to call 9-1-1. While the symptoms of stroke may vary depending on the individual, these major signs are a good indication that you or someone you know may be having a stroke. If you think someone is having a stroke, don’t wait to see if the symptoms go away.
According to the American Stroke Association time is of the essence when it comes to stroke treatment, so getting medical help as soon as possible is essential. By being aware of the symptoms of stroke and acting quickly if they occur, you can help to minimize the damage caused by this potentially life-threatening condition.
People who smoke or have high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or a sedentary lifestyle are in direct proportion and more likely to suffer a heart attack, cardiac arrest, and stroke. All individuals should be aware of the signs, particularly those with any of these risk factors.
Finally, if you are with someone who appears to be having a heart attack or stroke, calling 9-1-1 is paramount. There is no cure nor a home remedy for a heart attack or stroke. The greatest thing to do is get professional assistance as soon as possible.